Seminal AI Papers
The original AI papers were all about training, super technical, and not that usable as a practioner. Now a days papers are less “mathy” and more applicable to practioners. Here are some worth reading
LLM Agents
Woah, this starting off point is great:
From Lilian Weng’s LLM Powered Autonmous Agents
Shamelessly inlining from the above:
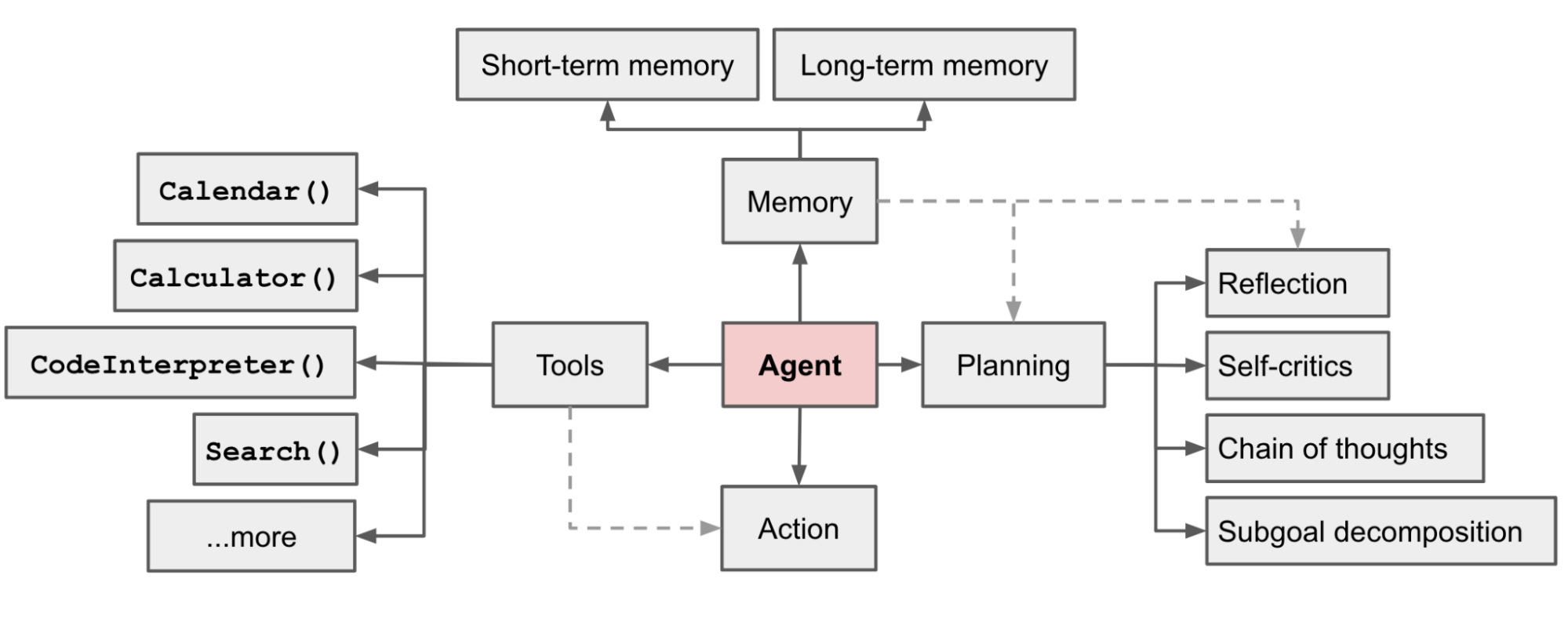
In a LLM-powered autonomous agent system, LLM functions as the agent’s brain, complemented by several key components:
Planning
- Subgoal and decomposition: The agent breaks down large tasks into smaller, manageable subgoals, enabling efficient handling of complex tasks.
- Reflection and refinement: The agent can do self-criticism and self-reflection over past actions, learn from mistakes and refine them for future steps, thereby improving the quality of final results.
Memory
- Short-term memory: I would consider all the in-context learning (See Prompt Engineering) as utilizing short-term memory of the model to learn.
- Long-term memory: This provides the agent with the capability to retain and recall (infinite) information over extended periods, often by leveraging an external vector store and fast retrieval.
Tool use
- The agent learns to call external APIs for extra information that is missing from the model weights (often hard to change after pre-training), including current information, code execution capability, access to proprietary information sources and more.
Security
Adverserial Attacks on Aligned Models
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.15043.pdf
TL;DR Researchers have developed a method to make language models generate objectionable content. They found that their approach of adding specific suffixes to queries can induce objectionable responses from various language models, including publicly released ones. This raises concerns about how to prevent language models from producing objectionable information.
Key Takeaways:
- Language models can generate objectionable content, and efforts have been made to prevent this.
- Previous adversarial attacks on language models have been limited in success and required human ingenuity.
- The researchers propose a new method that automatically generates adversarial suffixes to make language models produce objectionable behaviors.
- The generated adversarial prompts are transferable to different language models, including publicly released ones.
- GPT-based models are more susceptible to this attack, possibly due to their training on outputs from similar models.
- This research highlights the need to address the potential for language models to generate objectionable information.
Journaling Prompts:
- How can language models be effectively aligned to prevent the generation of objectionable content?
- What are the ethical implications of language models being able to generate objectionable information?
- Do you think it is possible to completely prevent language models from producing objectionable content? Why or why not?
- How can the findings of this research be used to improve the safety and reliability of language models?